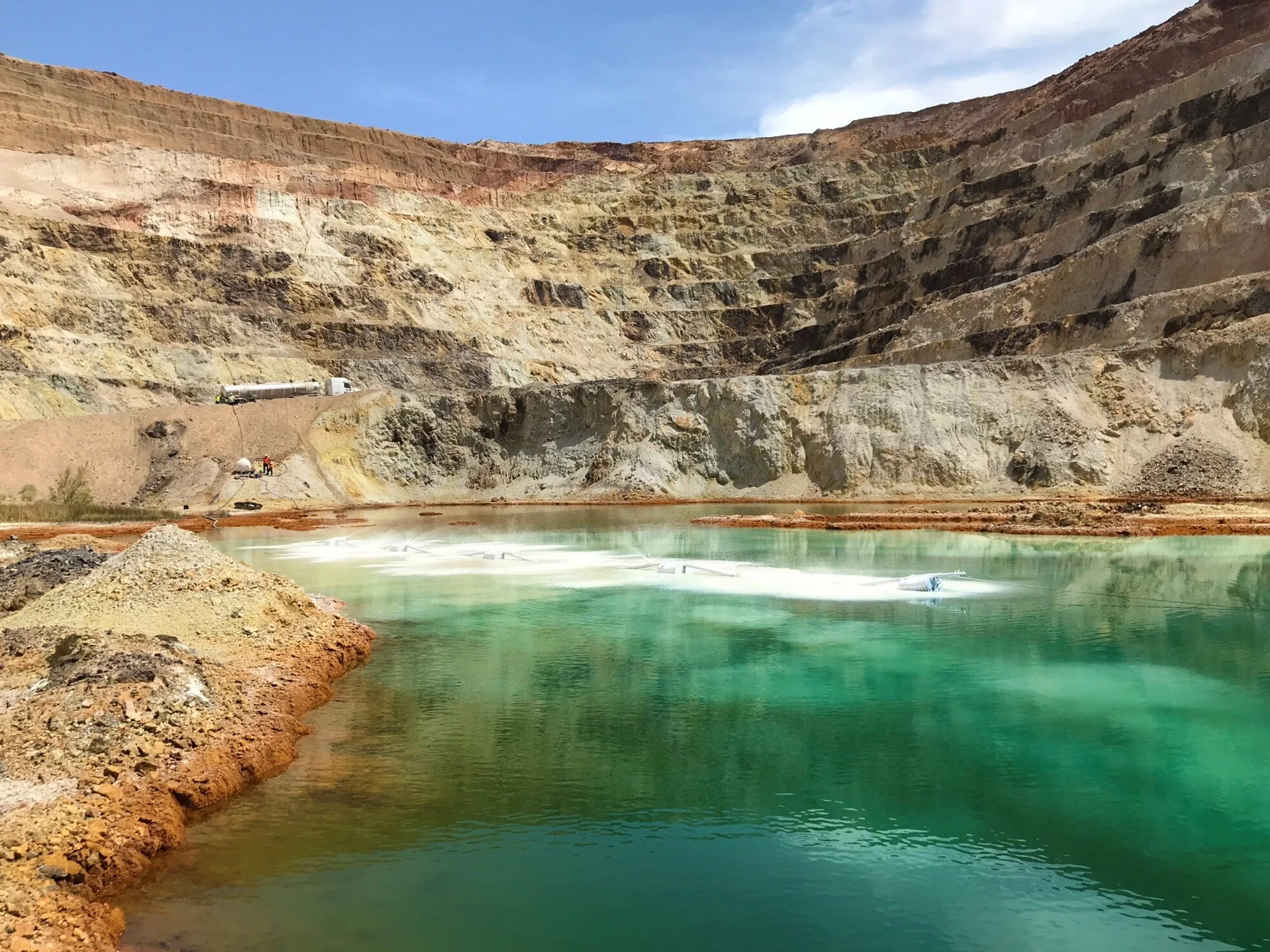
The development and management of pit lakes left behind after mining is one of the most significant issues facing the global mining industry. HydroGeoLogica takes a pragmatic approach to pit lake evaluation and management, evaluating critical paths and drivers to identify potential financial, social, environmental, and regulatory risks and opportunities.
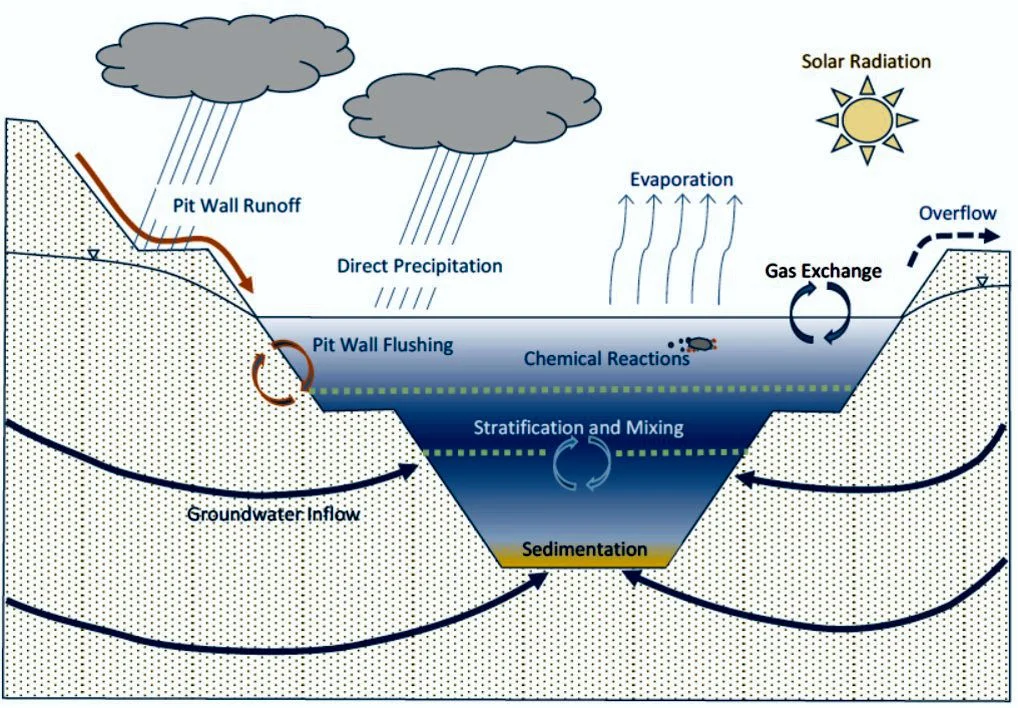
Generalized Pit Lake Conceptual Model
HydroGeologica’s pit lake evaluation begins with developing a conceptual model of the pit and its surroundings.
A pit lake water balance is constructed to predict inflows, outflows, and lake surface elevations through time. Water balance models are typically built using a dynamic systems model such as GoldSim, a stochastic modeling platform (Mine Water Management). When necessary, we link the GoldSim water balance model directly to PHREEQC, the reactive geochemistry model, using a proprietary customized DLL code.
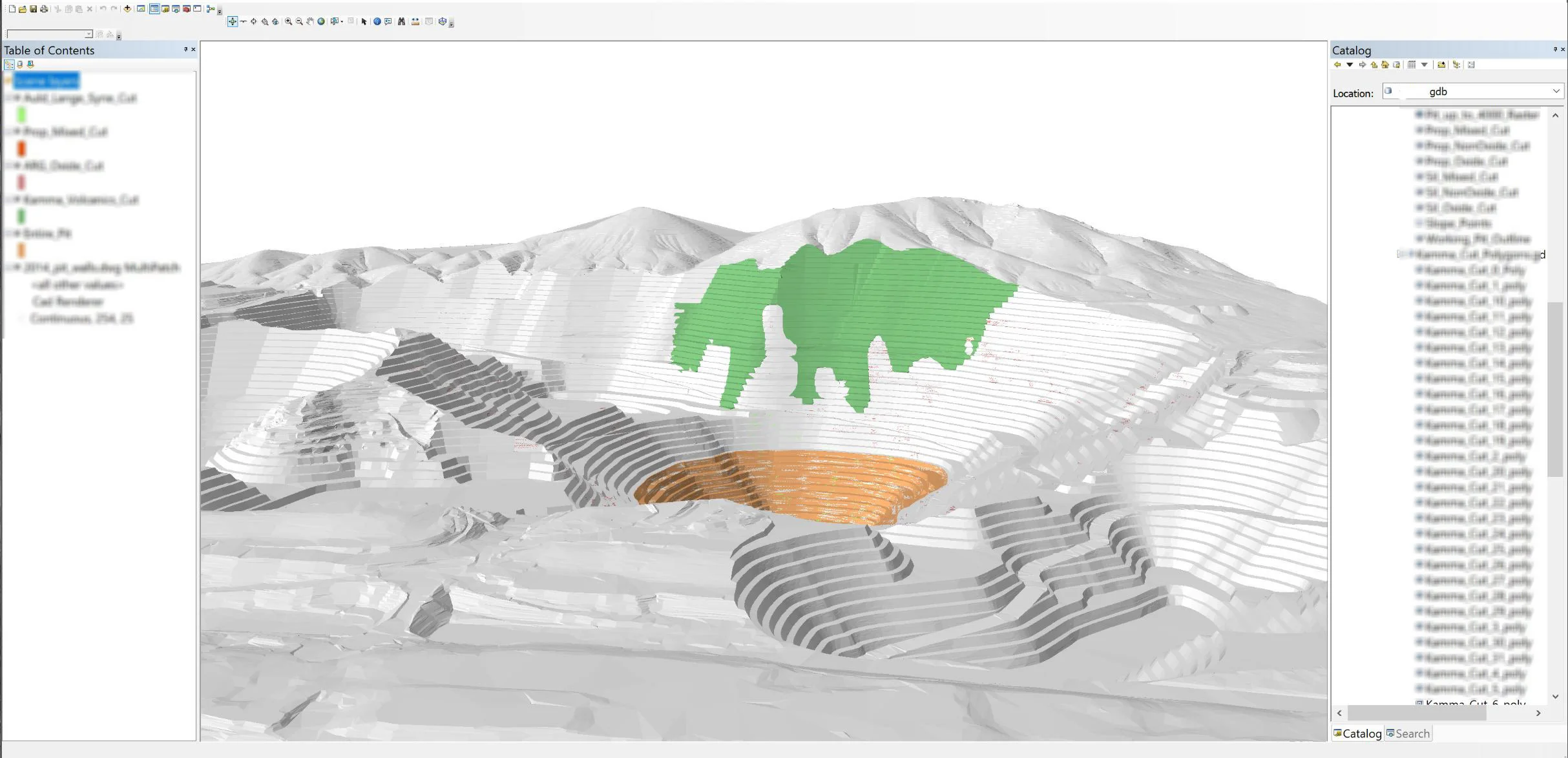
ArcGIS to Generate Surface Alteration Data for Geochemical Modeling
A geochemical model of the pit lake is constructed to represent the following geochemical mechanisms:
Chemical mixing and mass balance, including flushing of solutes from rock types in the pit wall as the water level rises
Evaporative concentration
Mineral equilibria
Sorption reactions
Reaction kinetics
Gas exchange with the atmosphere
Reduction/oxidation reactions
The pit lake chemistry is simulated through time as the pit fills, then as the water chemistry evolves after filling. A screening level risk assessment is conducted to determine if additional management of the pit lake is likely to be required to meet regulatory and closure requirements. Multiple management options can be simulated, such as:
Pit backfill
Rapid filling
Passive treatment
Water treatment
Pumping
Grout curtains
Forced stratification
Water disposal
Alkali amendment
Ferric amendment
Organic/nutrient amendment
Cost, risk, and benefit are evaluated for decision making to identify the most cost-effective and sustainable alternative(s). Pit lake monitoring provides real-time feedback to adjust and fine tune the closure plan during the dynamic filling phase to optimize management and long-term costs.